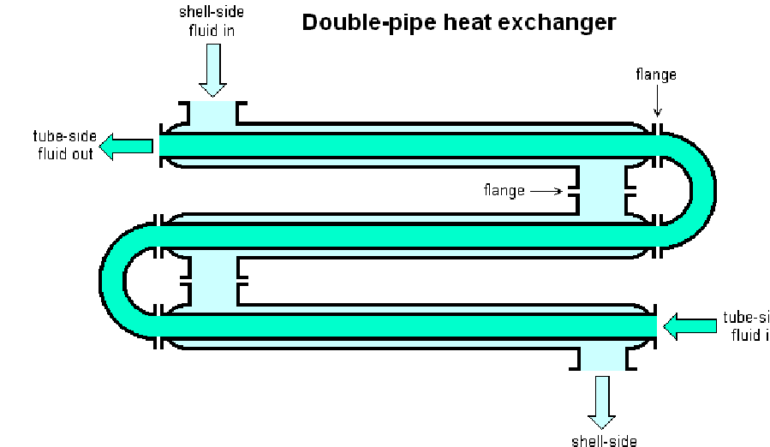
Double Tube Heat Exchanger
Double Tube Heat Exchanger is a type of Heat Exchanger that has a central conductive barrier that prevents both flowing liquids and an adjoining pipe from creating an annulus shape. The outer half of the pipe acts as a conductor, while the inner half carries the working fluid. The resulting heat exchange occurs through the inner tube. The hot flow goes through the inner tube while the cold flow goes through the outer shell. The double pipe heat exchanger is commonly used in counterflow, where the opposite direction of the flow is used. Double pipe exchangers are commonly used for high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to their ability to expand and have solid construction. However, they may also experience temperature cross during counterflow when the hot flow exceeds the cold flow. A double pipe heat exchanger is usually used in applications where the traditional shell and tube exchangers are not powerful enough to provide the necessary heat transfer. It can be used in parallel or in series to increase the temperature.
Application of Double Tube Heat Exchanger
⦁ Chemical Processing: Used for heating or cooling process fluids in chemical reactors, ensuring optimal reaction temperatures.
⦁ Oil and Gas Industry: Employed in crude oil heating for viscosity reduction, as well as in cooling systems for various fluids.
⦁ HVAC Systems: Utilized for heating and cooling air or water in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
⦁ Food and Beverage Industry: Used for pasteurization processes, where heating or cooling of liquid food products is required.
⦁ Power Generation: Applied in condensers and coolers in power plants, facilitating heat exchange between steam and water.
⦁ Pharmaceuticals: Used in processes that require precise temperature control to maintain product integrity during manufacturing.
⦁ Water Treatment: Employed for heating or cooling water in treatment processes, such as in swimming pools or industrial wastewater treatment.
⦁ Refrigeration: Used in systems where heat rejection or absorption is necessary, such as in chillers.
⦁ Marine Applications: Common in ships for cooling engine lubricants and in ballast water treatment systems.
⦁ Pulp and Paper Industry: Applied for heating and cooling processes in the production of paper products.
These applications leverage the double pipe heat exchanger’s ability to efficiently transfer heat between two fluids, making it a critical component in many thermal management systems.
Characteristics of Double Tube Heat Exchanger
- Can have counter-current flow throughout the length of the exchanger, which is ideal for handling a temperature cross.
- Provides a low flow area for both the shell and tube sides, making it suitable for very low flow rate applications. This ensures enough velocity to achieve good heat transfer coefficients and mitigate fouling, if applicable.
- Features a simple, compact design, making it ideal when the required heat transfer area is less than 10m². For larger requirements, multiple stacks or a longer exchanger may be necessary.
Advantages of Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers
- A double-pipe heat exchanger has a compact design, making it suitable for installations where space is limited.
- Double-pipe heat exchangers can handle various fluids, including liquids, gases, and mixtures. This versatility makes them suitable for different applications where various substances must be cooled or heated.
- These heat exchangers offer flexibility in terms of flow configurations. Depending on the process’s specific requirements, they can be arranged in parallel or counterflow arrangements. This flexibility allows for optimal heat transfer and efficiency.
- Double-pipe heat exchangers are relatively easy to maintain. The two pipes can be easily accessed for cleaning, inspection, or repairs. This ease of maintenance reduces downtime and ensures the heat exchanger’s long-term reliability. Therefore, double-pipe heat exchangers are often cost-effective for small-scale applications since simpler design and construction result in lower manufacturing costs.
- By utilizing a counter-current flow arrangement, they can achieve a greater temperature differential between the hot and cold fluids, maximizing heat transfer efficiency and providing effective temperature control.
- Double-pipe heat exchangers can be easily scaled up or down to meet the specific requirements of different applications, making them suitable for large chemical processing plants to small laboratory setups.